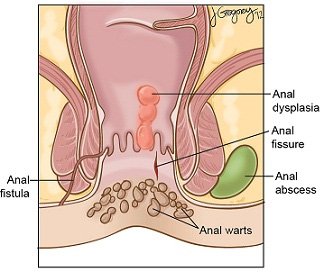
Anal warts are small, flesh-colored or pink growths that appear in and around the anus due to an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can be flat or raised and may grow in clusters over time. While anal warts are generally painless, they can cause itching, irritation, and discomfort if left untreated. These warts can spread to the genital area and increase the risk of complications, making early medical attention crucial.
If left untreated, anal warts can grow in size, spread to nearby areas, and become increasingly difficult to treat. In some cases, they may lead to chronic irritation, secondary infections, or discomfort during bowel movements. Additionally, certain strains of HPV linked to anal warts are associated with a higher risk of anal cancer, making early detection and removal essential. While some warts may remain small and cause minimal symptoms, others can multiply and form large clusters, significantly impacting a person's quality of life and self-confidence. Seeking prompt medical attention ensures effective treatment, prevents recurrence, and reduces the risk of complications.